Fish scraps might not top the list of appealing fertilizers, but their ability to enrich soil, deliver essential nutrients like nitrogen, and reduce organic waste makes them a valuable resource for gardeners. By understanding how to manage potential challenges such as odors, pests, and pathogens, you can harness the benefits of fish scraps safely and effectively. Discover four creative ways to use fish scraps in your garden and boost plant growth naturally.

The Power of Fish Scraps in Gardening
For centuries, gardeners have turned to fish scraps to nourish soil and support plant growth. As the scraps decompose, they release vital nutrients that enhance soil health and fertility. However, careful handling is essential to avoid potential risks. Here’s a breakdown of their pros and cons:
Benefits of Fish Scraps:
- Nutrient-Rich: Fish scraps are a natural source of nitrogen, calcium, potassium, and other trace minerals essential for plant growth.
- Soil Enrichment: They add organic matter, improving soil structure and moisture retention.
- Waste Reduction: Utilizing scraps reduces food waste and contributes to sustainable gardening practices.
Challenges of Fish Scraps:
- Pathogens: Raw fish can harbor bacteria and parasites that may contaminate soil or crops.
- Pests: The odor of decomposing fish can attract unwanted animals like raccoons, opossums, or pets.
- Heavy Metals: Trace amounts of mercury and other metals in fish could potentially impact soil quality.

Four Effective Methods to Use Fish Scraps
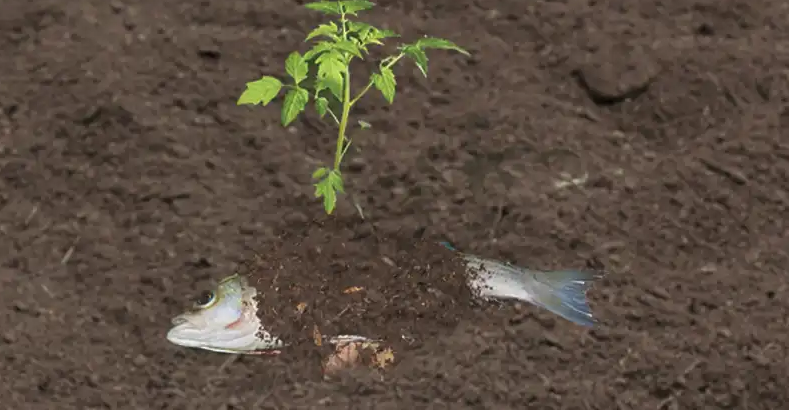
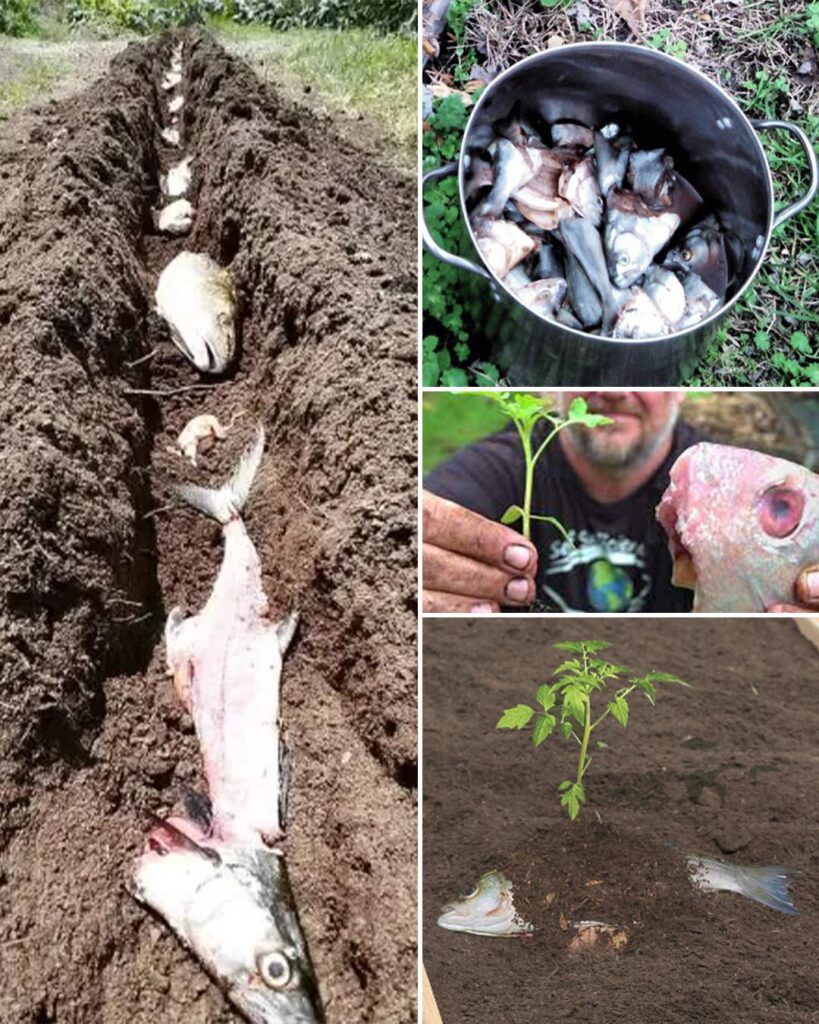
1. Burying Fish Scraps Beneath Plants
Burying fish scraps is one of the oldest and most effective methods for natural fertilization. This technique is ideal for fruiting plants such as tomatoes and cucumbers.
- How to Bury: Dig a hole at least 12-24 inches deep and place the fish scraps inside. Cover them with soil to mask odors and deter animals.
- Why It Works: The scraps decompose directly beneath the plants, delivering nutrients to the root zone. Gardeners often notice improved growth, higher yields, and healthier plants.
- Pro Tip: Avoid using this method near root vegetables or plants you consume in their entirety to minimize contamination risks.
2. Blending Fish Scraps for Fertilizer
For a quicker release of nutrients, blending fish scraps with water creates a homemade fertilizer.
- How to Blend: Add fish scraps to a blender with water and process until smooth. Pour the mixture lightly over the soil near your plants.
- Caution: The smell can be intense, so avoid using this method near heavily trafficked areas. Adding mulch afterward can help mask odors.
- Benefits: The finely blended mixture decomposes faster, offering a rapid nutrient boost to your plants.
3. Crafting Fish Emulsion
Homemade fish emulsion is a versatile liquid fertilizer that’s easy to use and store.
- How to Make Fish Emulsion: Combine fish scraps, sawdust, water, and a cup of molasses in a bucket. Stir daily and allow the mixture to ferment for two weeks. Strain the liquid, dilute it with water (1 tablespoon per gallon), and use it to water plants.
- Why It’s Popular: Fish emulsion provides quick-acting nutrients, making it perfect for fertilizing vegetables and flowering plants. It’s less likely to attract pests when properly diluted.
4. Composting Fish Scraps
Adding fish scraps to your compost pile is another sustainable way to recycle this resource.
- How to Compost Safely: Place scraps in the center of your compost pile to minimize odors. To eliminate pathogens, maintain the pile’s temperature at 145°F (64°C) for at least five days, repeating this process three times.
- End Result: Fish-enriched compost creates humus with improved soil conditioning properties, though it won’t drastically increase nitrogen levels.
Tips for Safe and Effective Use
- Source Responsibly: Use scraps from sustainably caught or organic fish. Stick to inedible parts like bones, heads, and organs.
- Avoid Overloading: Excessive fish scraps can overwhelm soil microorganisms and cause imbalances.
- Monitor Pests: Use deterrents or fencing to keep animals away from buried or composted scraps.
Alternative: Store-Bought Fish Fertilizer
If handling raw fish scraps feels daunting, consider using commercially processed fish fertilizers. Available in meal, emulsion, or hydrolysate forms, these products are pathogen-free and easy to apply. They offer many of the same benefits without the risks associated with raw fish.
Conclusion
Fish scraps offer a natural, nutrient-packed solution for enriching your garden’s soil. Whether you choose to bury them, blend them, create an emulsion, or compost them, each method has unique advantages suited to different gardening needs. With proper care and a bit of experimentation, you can transform kitchen waste into a thriving garden oasis. Embrace this eco-friendly approach and watch your plants flourish.
Inspired by this? Share the knowledge with your fellow gardening enthusiasts!