Taking care of your thyroid gland is essential for maintaining your metabolism, energy levels, and hormonal balance, especially as you age. While dietary supplements are widely used to support overall health, some popular options may unintentionally disrupt thyroid function. Let’s explore which supplements might be putting your thyroid at risk and how to use them safely.
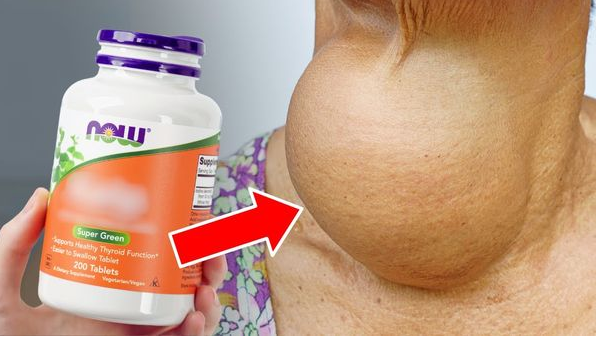
The Hidden Dangers in Common Supplements
Iodine
Iodine is critical for thyroid hormone production, but too much can be harmful. Excessive iodine intake may increase the risk of thyroid autoimmunity and disrupt normal thyroid function. Many people unknowingly consume high levels of iodine through supplements, despite already meeting their needs through diet.
Soy
Soy supplements and isoflavones can interfere with thyroid hormone absorption. They may block the enzyme needed to synthesize thyroid hormones, particularly in individuals with existing thyroid conditions.
Calcium and Iron
Calcium and iron are vital minerals, but they can reduce the absorption of thyroid medications if taken together. To avoid this, it’s best to take calcium or iron supplements at least four hours after your thyroid medication.
Kelp and Other Seaweeds
Kelp is naturally rich in iodine, making it a potential thyroid disruptor. Consuming kelp supplements without monitoring your iodine intake can easily exceed the recommended daily allowance, leading to thyroid dysfunction, especially in those sensitive to iodine.
Ashwagandha
This adaptogenic herb is popular for its stress-relieving properties, but it may unexpectedly boost thyroid hormone levels. While beneficial for some, ashwagandha could cause complications in people with thyroid disorders by increasing hormone production beyond normal levels.
How to Protect Your Thyroid Health
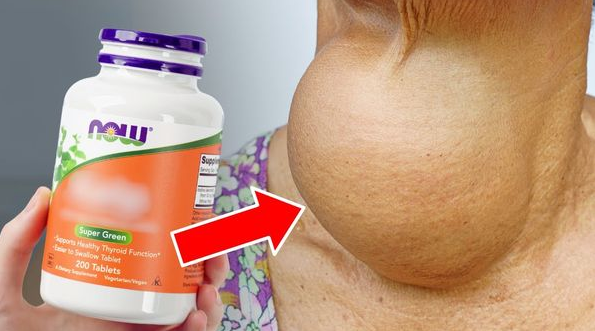
1. Monitor Supplement Dosages
Ensure that your supplement intake aligns with your actual nutritional needs. Excessive supplementation, even with beneficial nutrients, can have adverse effects, particularly on your thyroid.
2. Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Always discuss your supplements with a healthcare professional, especially if you have a thyroid condition. They can guide you on safe dosages and identify potential interactions with your thyroid medication.
3. Read Labels Carefully
Take time to review supplement labels. Be vigilant about ingredients like iodine or soy isoflavones, which may impact thyroid health, and ensure you’re not exceeding recommended daily allowances.
4. Schedule Thyroid Check-Ups
Regular thyroid check-ups help track your gland’s function and detect any issues early. This allows your healthcare provider to adjust your treatments or supplements as needed.
5. Balance Your Diet
A well-rounded diet can often provide the nutrients your thyroid needs without supplementation. Focus on whole foods rich in essential vitamins and minerals to support thyroid health naturally.
Conclusion
Supplements can play a vital role in addressing dietary gaps, but they must be used with caution to avoid unintended harm to your thyroid. By staying informed, consulting healthcare professionals, and carefully managing your supplement regimen, you can support your overall health while safeguarding your thyroid function. A healthy thyroid is key to a vibrant and energetic life—so make informed choices and prioritize your well-being!





